4.1: Lorentz Transformation And Lorentz Drive – Physics LibreTexts
Warning: Undefined variable $PostID in /home2/comelews/wr1te.com/wp-content/themes/adWhiteBullet/single.php on line 66
Warning: Undefined variable $PostID in /home2/comelews/wr1te.com/wp-content/themes/adWhiteBullet/single.php on line 67
|
| Articles Category RSS Feed - Subscribe to the feed here |
|
|
These circumstances may be related to the similarity lessons of Table 3.2. Within the case (i) \(F\) is unimodular axial, for (ii) it is nonaxial singular. (Since F is traceless, the 2 other entries in the table do not apply.) We first dispose of case (ii). A area having this Lorentz invariant property is called a null-area. The F matrix generates an exceptional Lorentz transformation (Part 3.4.4). In this subject configuration \(\vecE \text and \vecB\) are perpendicular and are of equal size. This is a relativistically invariant property that is characteriestic of airplane waves to be discussed in Section 4.2.
Think about standing on the ground of a rocket ship. There aren’t any windows. You are feeling your weight against the floor. For those who attempt to lift your foot, it wants to return down. So perhaps your ship is on the ground. However it’s also potential that your ship might be flying. If it is moving upward at a sooner and faster velocity – accelerating smoothly by just the right amount – your feet will feel pulled to the ground just as that they had when the ship was sitting on the bottom.
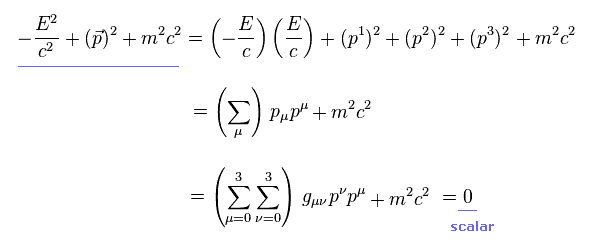
– Time goes more slowly at lower gravitational potentials. This is called gravitational time dilation.
– Orbits precess in a means unexpected in Newton’s theory of gravity. (This has been observed within the orbit of Mercury and in binary pulsars).
– Even rays of gentle (that are weightless) bend within the presence of a gravitational field.
– The Universe is expanding, and the far components of it are moving away from us faster than the velocity of light. This doesn’t contradict the speculation of particular relativity, since it’s space itself that’s expanding.
– Frame-dragging, through which a rotating mass “drags along” the area time around it.
Technically, general relativity is a metric theory of gravitation whose defining characteristic is its use of the Einstein subject equations. The options of the field equations are metric tensors which define the topology of the spacetime and the way objects transfer inertial.
With all these different frames of reference, can we ever know something for sure? The equations of relativity assist physicists basically ?translate? from one point of view to a different. Relativity helps us see the underlying info of a situation, even if its appearance can change vastly depending on point of view. So even though understanding that ?it?s all relative?
Now identifying a symmetry depends on two ideas, the transformation or relationship between totally different factors (or potentia in things), and the statement that two bodily configurations are equal. As a structural realist, Professor Feser would agree that there must be something corresponding to the transformation in physical reality if the physical description is accurate. Equally, if two configurations are equal in reality, if it is to be in any way accurate, they should also be so regarded in the abstracted representation (and if they are not equal, they have to be distinct in the representation). Thus if we have to construct the illustration with a selected symmetry so as to make it line up with reality, then that symmetry should also be current in reality. So in case you give the idea of structural realism to a contemporary physicist, ローレンツ変換 終焉 part of what he will do to break it down into one thing he can work with is to demand that each actuality and the physical abstraction ought to respect the same symmetries.
Find more articles written by
/home2/comelews/wr1te.com/wp-content/themes/adWhiteBullet/single.php on line 180